- September 16, 2021
- Bartarclinic
- Comment: 0
- Articles
What causes Genu Varum and what are the consequences of Genu Varum if left untreated
What is Genu Varum?
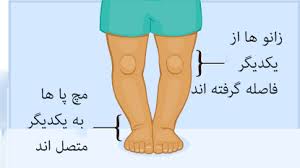
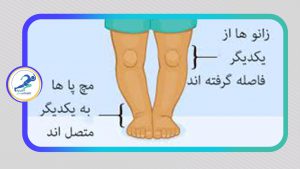
In the normal state, when a person is standing and their knees are straight and their ankles are touching each other, there shouldn’t be a significant gap between the knees. If there is an increased gap between the knees, it is called Genu Varum. When a person has Genu Varum, the shins deviate outward, the ankles turn inward, and the feet take on a bow-legged appearance.
Causes of Genu Varum
Muscular weakness
Vitamin D deficiency
Rheumatism
Bone fractures
Rickets (softening of bones)
Rotation of the legs inward
Excessive use of diapers during infancy
Overweight and obesity in children
Poor sitting and standing postures
Weakness or shortening of the hamstring muscle
Lack of coordination in growth plates
Early walking in children
Impact injuries to the knees
Arthritis or osteoarthritis
Fractures at the ends of the thigh bone that have healed poorly
Genu Varum leads to the following consequences :
Excessive wear on the sides of shoes
Early onset of pain and fatigue
Waddling gait
Rotation of the shins
Weakness in outer muscles, such as the Tensor Fasciae Latae muscle, Vastus Lateralis muscle, and Gracilis muscle
Shortening of inner muscles, such as the semimembranosus, semitendinosus, rectus femoris, and sartorius
Tightening of external knee ligaments and capsules and shortening of internal knee ligaments and capsules and the ankle
Decreased lower limb height
Change in the angle of the patellae and their inward inclination
Genu Varum in Infants:
Genu Varum is completely normal in newborns. Over time, the infant can bend and straighten their legs, maintain balance, and stand easily. At three to six months of age, Genu Varum is not observed, but most infants with Genu Varum are identified around eight months of age. If an infant continues to have this issue until age three or faces difficulty standing and walking, they should consult a physician.
Mild degrees of Genu Varum are common in children and usually do not require treatment. However, if the deformity persists beyond childhood, treatment is necessary. The best time to treat Genu Varum in children is when the condition does not correct itself with walking. In such cases, a consultation with an orthopedic specialist is recommended.
If Genu Varum is diagnosed in children before the age of four, non-surgical treatments are utilized, including
Custom orthoses for knees, ankles, and feet
Suitable orthopedic shoes
Prescribed vitamin D and a diet rich in calcium and phosphorus
Physiotherapy and stretching exercises
Characteristics of an Orthopedic Insole
Surgery is performed for children in severe cases and when non-surgical methods are ineffective. Surgical procedures are usually carried out after the growth plates have been closed, especially in severe cases in adults.
If left untreated, with increasing age, the likelihood of knee joint damage leading to knee arthritis exacerbates. Therefore, in cases of severe Genu Varum, where knee arthritis has developed, the possibility of knee joint replacement may be considered.
For more information and to contact the clinic, please visit the “Contact Us” section