- June 21, 2021
- Bartarclinic
- Comment: 0
- Articles, مقالات
Flat Sole of the Foot or Flatfoot
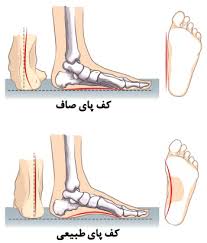
A flat sole of the foot is a condition in which individuals lack the normal arches in their feet. The existing arches in the foot reduce the forces exerted from the ground to the body and prevent all these forces from entering the body. However, in individuals with a flat foot, a considerable amount of these forces is exerted towards the body due to the absence of the foot arch. In the long run, it can lead to the development of chain-like complications in all joints of the body, especially the spine.
The problem of a flat foot is usually congenital and is also known as joint laxity. Joint laxity in the sole area causes the foot arch to disappear when standing on the foot. Additionally, the incomplete formation of one or two bones in the ankle and sole of the foot area, or their fusion together congenitally, also contributes to the lack of formation of the arch of the foot. This type of flat sole is called a flexible flatfoot.
Symptoms of a Flatfoot
- Pain in the ankle, the malleolus, or calf
- Painful or fatigued sensation in the ankle or calf after prolonged standing or walking
- Pain that occurs after exercising or engaging in other physical activities
- Swelling on the inside of the ankle
- Inward tilting of the shoe or the heel of the shoe
Complications of a Flatfoot:
Flatfoot can lead to complications such as plantar fasciitis, inflammation of the Achilles tendon and inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon, as well as stress fractures in the lower limbs and improper formation of dead skin tissues.
Since flatfoot also affects the alignment of other bones in the body, it can result in pain in the ankle, knees, and hips. Additionally, flatfoot can lead to long-term complications such as calcaneal spurs, knee pain, lower back pain, and headaches.
Symptoms and signs of this disorder include the appearance of a flat sole in one or both feet, inward tilting of the shoe or the heel of the shoe, pain in the lower limbs, pain in the ankle, swelling in the inside of the ankle, and pain in the ankle.
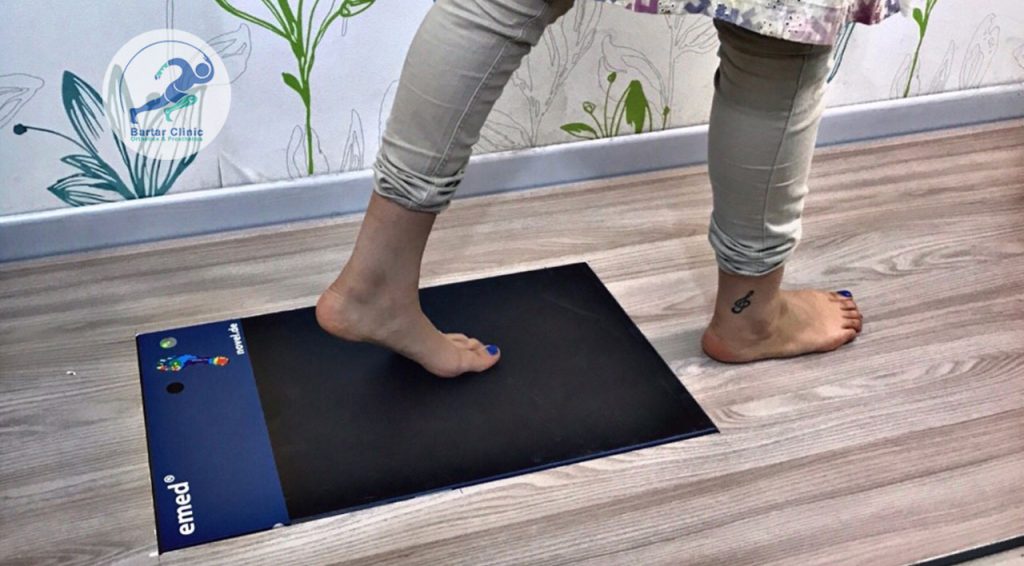
To view foot scan services and custom insole designs, click here.
Causes of Flatfoot:
- Congenital causes
Each foot is composed of 31 bones connected by 33 joints and over 100 muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Proper alignment of these components creates a natural arch in the foot. This arch must be both strong enough to bear the body’s weight and flexible enough to adapt to different surfaces.
Flatfoot can also result from weak muscles and connective tissues in the foot, excessive weight, or genetics, in which case various treatment options are available. - Sustained pressure on the foot: One type of pressure is the prolonged use of high-heeled shoes, which can negatively affect the Achilles tendon (the main tendon behind the heel) and disrupt the natural mechanical process of the ankle. Sometimes the compensatory function of the posterior tibial tendon can further exacerbate the issue, leading to progressive loss of the arch of the foot.
- Obesity
- Various injuries and impacts to the foot or ankle
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Environmental Causes:
Flatfoot Treatment:
If flatfoot does not cause specific walking symptoms in children, it usually corrects itself. However, if it does cause symptoms during walking, a specialized insole and brace should be created for the child.
Recommended rehabilitation methods and exercises for individuals with flat feet
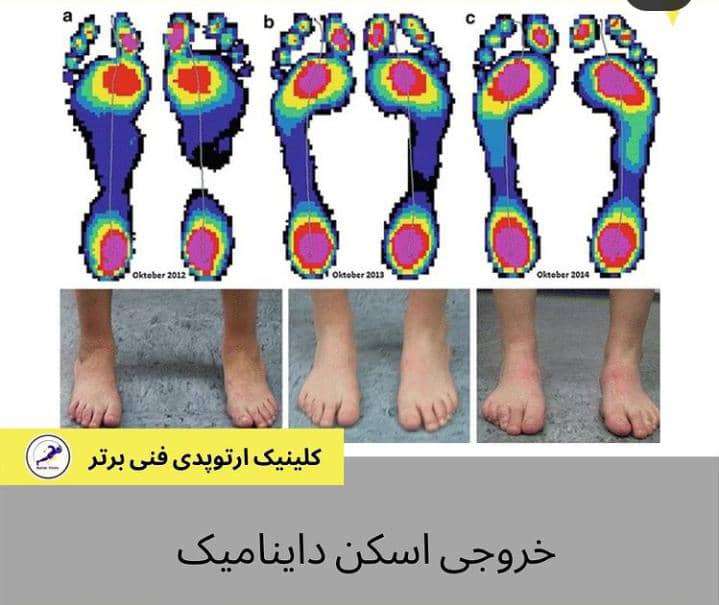
Custom orthopedic shoes (tailored to each patient) Custom orthopedic shoes are determined by a specialized physician and are made by orthopedic technical experts through plaster casting of the patient’s foot and creating a foot mold. Today, using a foot scan device, designing with its data, and making insoles with a CNC machine based on the pressure points of the foot are also used.

For more information and to contact the clinic, please visit the Contact Us section.